FAQ of USB Type-C and USB-PD
Time:2023-09-28
Views:479
FAQ of USB Type-C and USB-PD
USB-PD means USB Power Delivery.
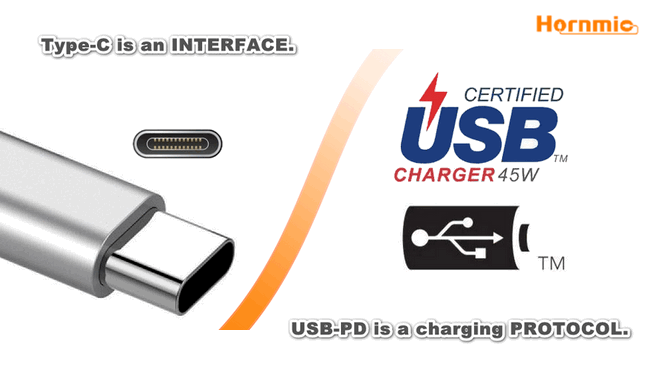
Q1 : What is the difference between USB Power Delivery (USB PD) and USB type-C?
- USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) is a protocol specification that supports up to 100W power transmission and data communication in one cable.
- USB Type-C is a reversible USB connector specification that supports lot of new standards, including USB 3.1 (Gen1 and Gen 2), Display Port, HDMI, and USB-PD, among others.
- The USB Type-C port can support up to 5V/3A (15W) power transmission by default, and up to 100W if USB-PD is implemented in the USB Type-C port. Therefore, the USB Type-C port does not necessarily support USB-PD.
Q2 : Is the USB Type-C connector mandatory for USB 3.1 Gen 1 or Gen 2 specifications and is USB Type-C equivalent to USB3.0/3.1?
While we can use traditional Type-A or Type-B connectors to support the Gen 1 and Gen 2 specifications, the USB Type-C specification is a new interface certification specification published by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) that supports up to 100W of power transfer and a reversible interface. All USB 3.1 Gen 1 or Gen 2 specification products can use the USB Type-C interface.
So our answer is that the USB Type-C specification and the USB 3.1 Gen1 or Gen 2 specification are independent of each other.
Q3 : What is the Configuration Channel (CC) and what is the maximum speed of the CC bus?
The CC bus is the data line used for USB-PD communication between the port and the EMCA.The USB Type-C plug has two pins CC1 and CC2, one of which is identified as the CC line based on the plug orientation of the USB Type-C connection.The CC line is fixed for USB Type-C plugs. The CC’s bit rate ranges from 270 Kbps to 300 Kbps and is rated at 300 Kbps.
CC has the following functions:
- Detects USB Type-C plug orientation to establish USB data bus routing.
- Detect USB port connections from the DFP to the UFP.
- Establish the role of the DFP and UFP between the ports.
- Find and configure VBUS.
- Configure VCONN.
- Locate and configure optional standby and accessory modes.
Q4 : What is the difference between USB-PD2.0 and Qualcomm QC fast charging?
USB-PD 2.0 is a charging protocol developed by USB-IF that provides a power supply mechanism between USB devices up to 100 W (20V, 5A) and the ability to support both USB and non-USB data signals on USB Type-C ports, allowing flexible negotiation of power direction between host and peripheral devices.
Qualcomm® Quick Charge™ is Qualcomm‘s proprietary charging protocol, using a custom charger that supports the Qualcomm Quick Charge protocol to charge devices that also support the protocol. Quick Charge 2.0 can transfer up to 60 W of power, but unlike USB-PD, Quick Charge 2.0 cannot support both power transfer Unlike USB-PD, Quick Charge 2.0 does not support both power and data transfer, nor does it support flexible power direction selection during charging.

Q5 : What is the maximum number of Power Delivery Objects (PDO) that can be supported by the USB-PD controller? What are the supported power profiles?
USB-PD supports up to 7 PDO‘s for pull current and fill current applications.
The USB-PD specification does not require which power profiles the application device needs to support. Pull-current and fill-current PDO‘s depend on the application design. section A.1 of the USB Type-C specification defines a standardized combination of voltage and different current ranges. it is important to note that the power profiles defined in section A.1 are only recommended power profiles, not mandatory, but at least one pull-current PDO that can be used to support 5V is required.
Q6 : Can I use only the USB function of the USB Type-C port and the standard 5V VBUS function?
Yes, you can only use the USB function of the USB Type-C port and the standard 5V VBUS function.
Host side: The default port currents provided by the host Type-C port for USB 2.0 (500mA) and USB 3.0 (900mA) are 5V 1.5A and 5V 3A, respectively. USB Type-C hosts indicate the current capacity by stringing an appropriate pull-up resistor Rp on the CC lines (CC1 and CC2).
Device side: Only USB Type-C devices are supported and require a 5.1K pull-down resistor Rd in series on the CC line. if the device is equipped with a USB Type-C plug, Rd needs to be in series on both CC1 and CC2 lines. however, if the device is equipped with a Type-C plug, Rd only needs to be connected on the CC line.
Q7 : How do USB Type-C devices handle VBUS voltages greater than 5V?
When a device requires a supply voltage greater than 5V, it requires the ability to communicate with USB-PD, which pulls current to send the power profile to the device, which then requests one of the installed power profiles based on its supply current capacity and establishes an agreement so that the host can provide the requested voltage on VBUS.
By HornmicLink_Bob Kuo @230928 11:58